|
|
|
|
|
A Comparative Study on the Effectiveness of Social Media Marketing Channels in Governance-Based Organizations
Anjali Singh 1![]() , Dr. Priya Satsangi 2, Dr. Bhawna Sharma 3
, Dr. Priya Satsangi 2, Dr. Bhawna Sharma 3
1 BBA
3rd Year, Amity Business School, Amity University Mumbai, Mumbai, India
2 Associate
Professor, Amity Business School, Amity University Mumbai, Mumbai, India
3 Director-International Affairs and
Programs, Officiating HOI, Amity Business School, Amity University Mumbai, Mumbai, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
Social media is now an integral part
of modern marketing and has greatly changed the way organizations
communicate, educate, and engage with their varied audiences at the same
time. For governance-based organizations, those dedicated to leadership
development, ethical training, and board governance, digital communication
still gives them a medium through which to establish themselves as visible
and credible. This research paper, named “A
Comparative Study on the Effectiveness of Social Media Marketing Channels in
Governance-Based Organizations” is about the comparative effects of the three
social media channels LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook on brand recognition,
professional engagement, and audience reach. It also clarifies which platform
provides the best marketing effect and professional value in the governance
sectors. The main data was the result of a
structured survey conducted with 20 employees at a governance-focused
advisory firm, while secondary data came from reports and academic studies.
The results indicate that the most appropriate platform for professional communication
and thought leadership is LinkedIn, that Instagram is the most suitable for
visual storytelling and engagement, while Facebook plays a supplementary role
and is effective at reaching a wider audience. The research recommends that firms
working with governance should implement a synchronized marketing strategy
that is based on the different platforms and which together incorporate
professionalism, creativity, and data analytics, thus building credibility
and digital impact. |
|||
|
Received 15 June 2025 Accepted 21 May 2025 Published 30 June 2025 DOI 10.29121/ShodhShreejan.v2.i1.2025.45 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Social Media
Marketing, Governance-Based Organizations, Linkedin Effectiveness, Instagram
Engagement, Facebook Outreach, Professional Networking, Audience Engagement,
Digital Communication. |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
Digital marketing has played an important role in creating an interaction between organizations and their stakeholders. For organizations that are governance-based, those that are mostly concerned with board leadership, ethics, and training, social media use goes beyond merely promoting. It is a tool that not only increases awareness of governance principles but also creates and develops thought leadership and invites professionals to participate in the learning process by sharing their thoughts and experiences.
Over the last few years, LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook, among others, have become the most widely used and significant communication tools. LinkedIn acts like a professional platform where people share their knowledge and interact with others in the same industry. allows visual representation of programs, workshops, and success stories, whereas Facebook remains a platform for people's interaction and discussion within the community.
The research examines the differences in the effectiveness of these three platforms in terms of the visibility, engagement, and positioning of the brand for governance-based organizations.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1. Digital Marketing in Governance Sectors
According to Chaffey and Ellis-Chadwick (2023), digital marketing organizations can possibly enable relationship development through online credibility and activity engagement. In governance-based firms, selling is not the objective; rather, it's educating and building trust. Kotler et al. (2022) have mentioned that digital channels assist professional bodies in showing expertise, ethics, and transparency.
2.2. LinkedIn and Professional Networking
It stands out as the leading networking platform for professional communication. LinkedIn (2024) shows that 80% of the B2B leads come from LinkedIn. According to Balaji (2023), governance companies use it to disseminate thought leadership content, including governance updates and training insights, to help them be perceived as credible authorities.
2.3. Instagram and Visual Storytelling
Tuten and Solomon (2023) identify that Instagram enhances engagement through visual content, reels, and infographics. To the governance firms, it aids in communicating on serious issues, such as leadership and ethics, in a lively way. Capurro (2023) supports the idea that visual storytelling increases authenticity and brand recall.
2.4. Facebook and Community Outreach
While its professional utility has declined, Facebook still enables awareness and community-building. KPMG (2024) remarks that organizations use it for event promotions and public communication; thus, it supports the core marketing channel as a secondary one.
3. IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING CHANNELS IN GOVERNANCE-BASED FIRMS
Organizations that focus on governance and leadership find that marketing channels offer a purpose beyond simple advertising. Rather than advertising, marketing channels can function as a centre for education, transparency, and stakeholder engagement and education. These channels allow firms to effectively communicate their expertise, mission, and ethical standards. Since such organizations are advisory in nature, the credibility of these organizations depends on how well they present their insights, programs, and principles to their target audience.
In recent years, LinkedIn has become the most important social networking site for professionals, enabling firms to share ideas related to good governance, training, and leadership. Facebook no longer leads such interactions, although it continues to be quite important in community involvement and brand awareness. Instagram allows highlighting of various initiatives, success stories, and event summaries in a modern, visually appealing style.
Collectively, these platforms provide governance-oriented organizations with an opportunity to:
· Building trust and authenticity in their professional audience.
· Promote governance training and leadership programs in a credible and effective manner.
· Encourage collaboration, learning, and professional growth.
· Establish them as voices in ethical leadership and corporate compliance.
4. RESEARCH GAP
Most of the research that has been done on social media marketing has concentrated on companies that sell to consumers or tech firms. Governance-based organizations, on the other hand, are very different since they prioritize empowerment and education over sales. Their marketing goal is not so much conversion as it is awareness and thought leadership.
In spite of this, not much research has been done on how leadership or governance firms use digital platforms to interact with professionals. Additionally, there aren't many comparative studies that evaluate Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn's performance for these kinds of organizations.
By examining the efficacy of social media platforms in promoting professional engagement, awareness, and credibility in governance-focused organizations, this study closes a gap in the literature.
5. PROBLEM STATEMENT
Networking with a small, specialized audience that values credibility over originality is a challenge for organizations in the governance space. Although social media offers a wide range of outreach tools, not all of them are made equally to serve the same function.
This study attempts to solve the problem of determining which social media platforms would be best for raising professional credibility, engagement, and brand awareness for companies operating in the governance sector.
6. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
· To identify the most used social media platform among employees.
· To determine the purpose for which different social media platforms are used.
· To analyze the frequency of social media usage among professionals.
· To understand engagement patterns on organizational social media content.
· To assess employees’ perceptions of marketing effectiveness.
· To gather suggestions for improving online presence.
7. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study uses a descriptive research design that will focus on interpreting real-world data through quantitative and qualitative analysis.
· Primary Data: Collected through a structured questionnaire distributed to 20 employees of a governance-focused advisory firm during an internship.
· Secondary Data: Obtained through journals, annual reports, and research publications regarding digital marketing and governance.
· Sampling Method: Convenience sampling was adopted, targeting those employees who were directly involved with or aware of the organization's social media initiatives.
· Tools and Techniques: Result interpretation was done through percentage analysis and graphical representation using pie charts.
8. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
The objective of this study is to understand the effectiveness of LinkedIn, Instagram and Facebook in governance-based organizations. It is based on primary data collected through a structured questionnaire from 20 employees working at an advisory firm focused on governance issues.
The responses offered an insight into the perceptions, level of engagement, and assessments by employees with regard to the organization's digital marketing practices. Data analysis was done through the percentage method and graphical interpretation (pie chart); this made trends clearly understandable.
Question 1:
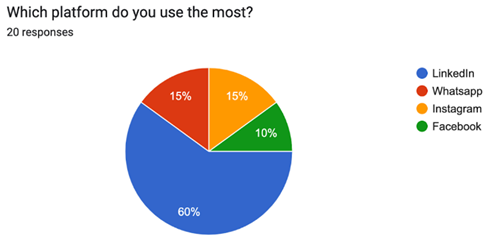
Choosing LinkedIn as the primary social media platform for approximately 60% of the surveyed employees is a clear indication that they primarily use social media for work purposes. The company needs to give the first place to LinkedIn in sharing news, posting about leaders, and providing information about its programs to the business professionals successfully.
Question 2:
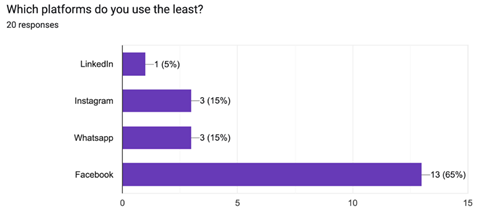
According to the graph above, 65% of the employees report that Facebook is their least used platform, and Instagram is their most used platform. This shows that employees are more active on LinkedIn as compared to other platforms, hence the most preferred professionally relevant channel.
Question 3:
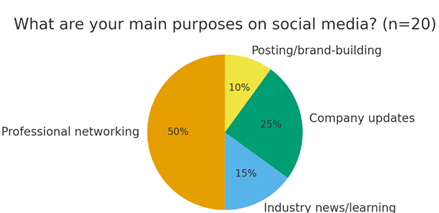
From the pie chart, the responses reveal that 50% employees mainly use social media for professional networking, which mainly means they connect, learn from experts, and grow in their careers. Only 10% chose posting and brand building; thus, it is the least common purpose for social media.
Question 4:
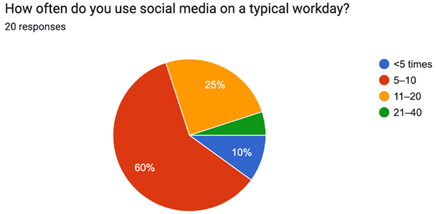
The above pie chart describes that the majority, around 60% of the workers, look at social media 5-10 times a day. It shows that throughout the day, people use social media quite frequently; hence, posting 1 to 2 quality posts daily would be ample to gain their interest. Additionally, with the help of short stories or reels, the audience can be kept active and interested during the day.
Question 5:
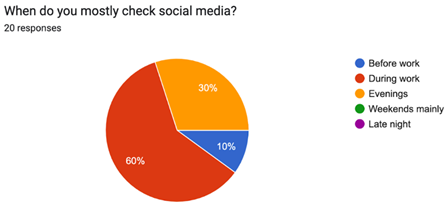
As per this chart, during work, about 60% of workers go onto social media. As such, posting on sites like LinkedIn is best just before or during business hours, basically around 9:00-11:00 AM and 2:00-4:00 PM. Share brief reels or recap posts later in the afternoon to keep users interested.
Question 6:
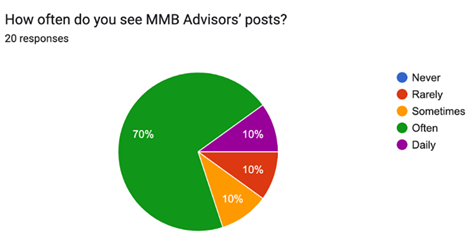
It indicates, from the graph, that 70% of participants reported that they frequently see the business's social media posts. This therefore means that employees already see the posts quite regularly, probably through the algorithm of the platform. In such a case, employees can be encouraged to reshare posts with pre-designed templates or captions in order to reach a larger audience than the company employees. The business entity can also use small promotions to boost visibility.
Question 7:
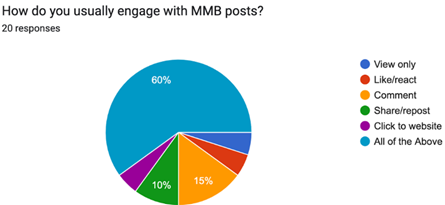
The chart shows that 60% of the respondents chose "All of the above", and this means that most of the employees interact with posts in many ways they like, comment, share, and click on the content. It indicates that employees are active and interested in the company's posts, especially when the content is relevant and appealing.
Question 8:
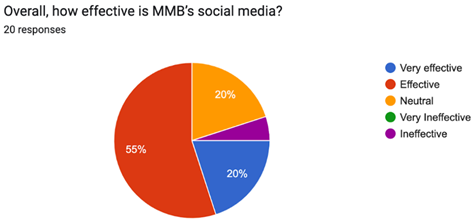
The chart shows that 20% of the respondents viewed the company's social media as very effective, and 55% believed it was effective. That means, though most people believe the company's social media presence is doing well, there is still room for improvement. In taking it to the next level, the business needs to come up with short yet interesting captions, use more apparent CTAs, and maintain a consistent visual style to draw in more clicks and inquiries.
Question 9:
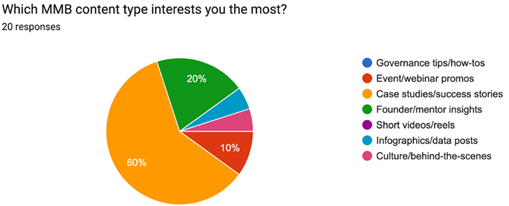
The chart shows 60% of the respondents are most interested in case studies and success stories-meaning people like to see real examples of achievement and positive results. To that end, success stories can be posted every month in the company. Each post shall include a short caption, a carousel of key points, and a link to the full story on the website. Adding a mentor quote and some measurable results will make it more engaging and trustworthy.
Question 10:
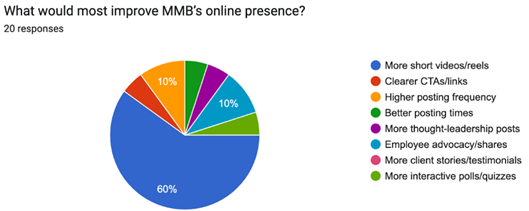
From the chart, 60% believe that creating more short videos or reels would most effectively enhance the company's online presence. That means visual, fast-paced, easy-to-view, and shareable content is preferred by people. The company can try a 4 to 6 week reel plan with 30 to 45 second clips featuring simple governance tips, event highlights, mentor insights, and brief success stories. To measure improvement, the company should track the number of views, saves, and new followers that come from these videos.
9. FINDINGS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Organizations based on governance consider LinkedIn as the strongest tool for professional communication, visibility, and thought leadership. It allows companies to interact with professionals and corporate leaders in a meaningful way and share knowledge-based content. Instagram contributes to the organization's visual engagement and presents the organization in a more relatable way before the audience. With the help of reels, stories, and visual highlights, the organization will have a better connection with its younger audience. Facebook has gradually decreased in its professional significance, but it is still a good channel for letting the community know about events and raising public awareness. Company posts get a lot of employee interaction, indicating a vibrant internal engagement and a healthy company culture.
Further analysis suggests that success stories, leadership insights, and short videos are actually the most favoured content types by the audience as they are the ones that create authenticity and trust-building. Current marketing strategies mostly prove to be working well, but there is still a need to make them more consistent, plan for better content, and employ the use of analytics for measuring performance. In more general terms, organizations with a governance focus should aim for a combination of trust, professionalism, and creativity through the use of storytelling and innovative approaches to their digital presence as a means of garnering long-term engagement.
Table 1
|
Platform |
Primary Audience |
Content Type |
Purpose |
Engagement Level |
|
Instagram |
Young professionals,
entrepreneurs, students |
Visuals, reels, stories |
Awareness and Engagement |
High |
|
LinkedIn |
Corporate leaders,
directors, business owners |
Articles, posts, events |
Professional Networking |
Moderate to High |
|
Facebook |
General public,
professionals, startups |
Posts, live videos, ads |
Awareness and Community
Building |
Moderate |
Social media marketing effectiveness in governance-centric organizations can be improved by the following recommendations that are based on the study:
1) Professional Outreach through LinkedIn: Governance content, such as tips, event highlights, and professional insights, should be communicated mainly through LinkedIn. The posting (4-5 times a week) in a thought-leadership tone will enhance brand credibility.
2) Instagram Visual Storytelling: Mentorship programs, training, and leadership events can be visually presented through Instagram reels, carousels, and infographics. Young professionals' engagement can be gained through reels with governance quotes or insights from the boardroom.
3) Utilization of Facebook: Facebook is not the most preferred social media platform in corporate engagement, but it is still good for announcing events and hosting live webinars. Consistency can be maintained by sharing posts from LinkedIn.
4) Content Calendar to be Structured: A regular posting calendar leads to continuous audience engagement. The calendar can have the following mix of contents: 40% educational, 30% interactive, 20% inspirational, and 10% promotional.
5) Support from Employees: Reposting of the organization's posts by employees should be encouraged. The process will be made easier through the creation of pre-approved “reshare kits” containing visuals and captions, which will lead to advocacy that is more effective and increased organic reach.
6) Adopt Analytics Tools: Engagement metrics like impressions, comments and clicks should be used to monitor engagement. LinkedIn insights and Meta Business Suite could help in improvement.
7) Maintain Visual Consistency: A uniform colour theme tone typography should be used to maintain professional identity across all social media platforms.
8) Use paid advertising selectively: A small budget should be allocated for posts and ads that focus on leadership and governance professionals to increase the outreach precision.
9) Foster Continuous Learning and Innovation: Latest trends and new formats should be regularly analyzed. The companies should stay updated on the algorithm changes to maintain relevance and audience engagement.
10. LIMITATIONS
This research contains information that is important but has various limitations, like:
1) Sample Size Limitation: This survey has included only 20 respondents, hence limiting the findings.
2) Restricted Platform Scope: The study examined only LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook, excluding platforms like YouTube and Twitter (X), which also influence digital marketing.
3) Short Research Duration: Conducted within a limited internship timeframe, the study does not capture long-term engagement patterns or changes in platform algorithms.
4) Self-Reported Data: Responses are based on employees’ self-assessment, which may include personal bias or social desirability effects.
5) Lack of External Audience Perspective: This research only included employees and not the stakeholders or customers
6) Basic Analytical Techniques: Descriptive and percentage analysis are used in this study. Several advanced tools, like regression or correlation, would be able to provide a deeper insight in the near future
7) Industry-Specific Focus: Only a governance-based organization is used in this research.
11. CONCLUSION
The analysis of the use of social media platforms has led to the conclusion that each platform serves a different purpose for governance-based organizations. Among them, LinkedIn is by far the most popular and efficient as it opens doors for professional networking, dissemination of expert knowledge, and establishment of a powerful and trustworthy brand image in the market. In contrast, Instagram is a platform where visual content, like reels and stories, has the most effect; therefore, this way, the organization is seen as more fun and relatable, especially to the younger generation. Facebook, though less formal, still plays a role in providing community updates and communicating about events.
On the whole, the company has a good social media presence at this point; the employees are really good at liking and sharing the posts. Still, there is the possibility of making things even better by being more consistent, using better visuals, and making more short videos. If authorities mix professionalism with a certain degree of creativity and post regularly, they will be able to secure strong trust, reach the right audience, and consequently have a powerful digital presence.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Chaffey, D., and Ellis-Chadwick,
F. (2023). Digital Marketing: Strategy,
Implementation and Practice Pearson.
Kotler, P., Keller, K. L., and
Chernev, A. (2022). Marketing Management (16th
ed.). Pearson.
Tuten, T. L., and Solomon, M. R. (2023). Social Media Marketing. SAGE Publications.
LinkedIn. (2024). B2B Marketing & Lead Generation Insights.
Meta Platforms, Inc. (2024). Social Media Performance and Engagement Report.
KPMG. (2024). Digital and Social Media Trends Report.
MMB Advisors Pvt. Ltd. (2024). Company Website & Annual Report.
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© ShodhShreejan 2025. All Rights Reserved.